Case study summary
As part of Apollo’s sustainability action plan, the group is tracking monthly energy consumption, total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, water withdrawal, waste generation, and commensurate emissions for 40 of its largest facilities, which account for 90% of the group’s total energy consumption, in efforts to set and measure improvement goals.
Demographic information
- City: New Delhi
- State/province/region: Delhi
- Country: India
- Type of institution: Private tertiary care hospital
- Number of full-time staff: 50,000
- Patient population served annually:
- ~4 million patients served annually
- Geographic area served: Pan India
- Number of beds: 10,000+
The Apollo Hospitals Group revolutionized quality health care in India by driving accreditation for a number of its hospitals through the Joint Commission and the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals and Healthcare Providers, the premier accreditation authority of health care accreditation in India.
The issue
A major challenge facing the health care group in decarbonization was the lack of standard data sets available. While each unit of the group was maintaining data on emissions, waste generation, and water, there was no aggregated data under a consolidated head.
To improve this issue, a robust, IT-driven platform was developed to aggregate data sets from all hospitals. This data was meant to serve as a baseline to identify decarbonization action plans.
Chief Engineer, Ahmedabad
"We found this platform to be very useful in measuring the data relating to environment. I have been very passionate to bring in data based management to make our hospital more green. This project will help a long way in achieving that."
Hospital goals
- Create a robust, IT-backed platform to capture sustainability aspects of operations.
- Ensure the collection of data includes energy consumption, Scope 1 and 2 emissions, waste generation, water use, and discharge, as well as Scope 3 data in subsequent years.
- Create a framework to ensure participation of key stakeholders and promote ownership by facility operators.
- Create a dashboard that can visualize data for each hospital to create targets and monitor progress.
Chief Engineer, New Delhi
"We have been robustly managing data on environment-related issues. I personally feel very strongly about bringing inefficiencies through the use of technology to reduce the healthcare sector’s footprint on our climate. Through this project, we could put this data to use for us to create targets and monitor progress. We will expand on this in the years ahead."
Sustainability strategy implemented
The sustainability team included corporate leadership, operations leadership, chief information technology officer, the chief finance officer, the chief of group compliance and company secretarial affairs, and the group lead for sustainability. This team reviewed and identified the best approach for standardizing and aggregating sustainability data from all facilities by assessing the merits and drawbacks of each possible strategy noted below.
- Enhancement of existing hospital information system to enable measurement of sustainability metrics.
- Creation of an in-house IT tool.
- Use of offline and static methodologies (such as Excel sheets and cloud file sharing) for data capture and consolidation.
- Partnering with an external IT solutions provider to develop customized software.
Having evaluated all available options available, leaders decided to partner with an external IT solutions provider to create a new platform. Various vendors were evaluated before a partner was selected for this project.
Implementation process
Chief Finance Officer contract approval was key to gaining buy-in from internal stakeholders including the board committee overseeing sustainability.
The group working on sustainability (GSL) and others began evaluating and modifying the SaaS-based software available through the partner firm, giving specific input on the group’s operations, scope, and current methodologies for reporting environmental data. Data available through published international repositories such as Health Care Without Harm and the United Nations were used to calculate emissions inventory and intensity.
The partner company created a customized solution for implementation in April 2022. GSL then presented this solution to the board committee overseeing sustainability initiatives. After their approval, implementation was initiated in May 2022 with a pilot phase at facilities in New Delhi and Ahmedabad. The pilot focused on team formation, standard operating procedures, data templates, data submission deadlines, capacity building, and training.
The sustainability team conducted a detailed outreach to relevant internal stakeholders including CEOs, heads of operations, chief engineers, IT leaders, the quality team, and the medical services head.
Through a series of workshops in all regions, relevant stakeholders were oriented to the platform. After this, each hospital was asked to identify a single point of contact and oversight mechanism. A detailed tutorial video was created for the operating teams. To reduce the carbon footprint from travel for orientation, e-meeting tools, WhatsApp groups, video calls, virtual tutorials, and written materials were employed.
Tracking progress
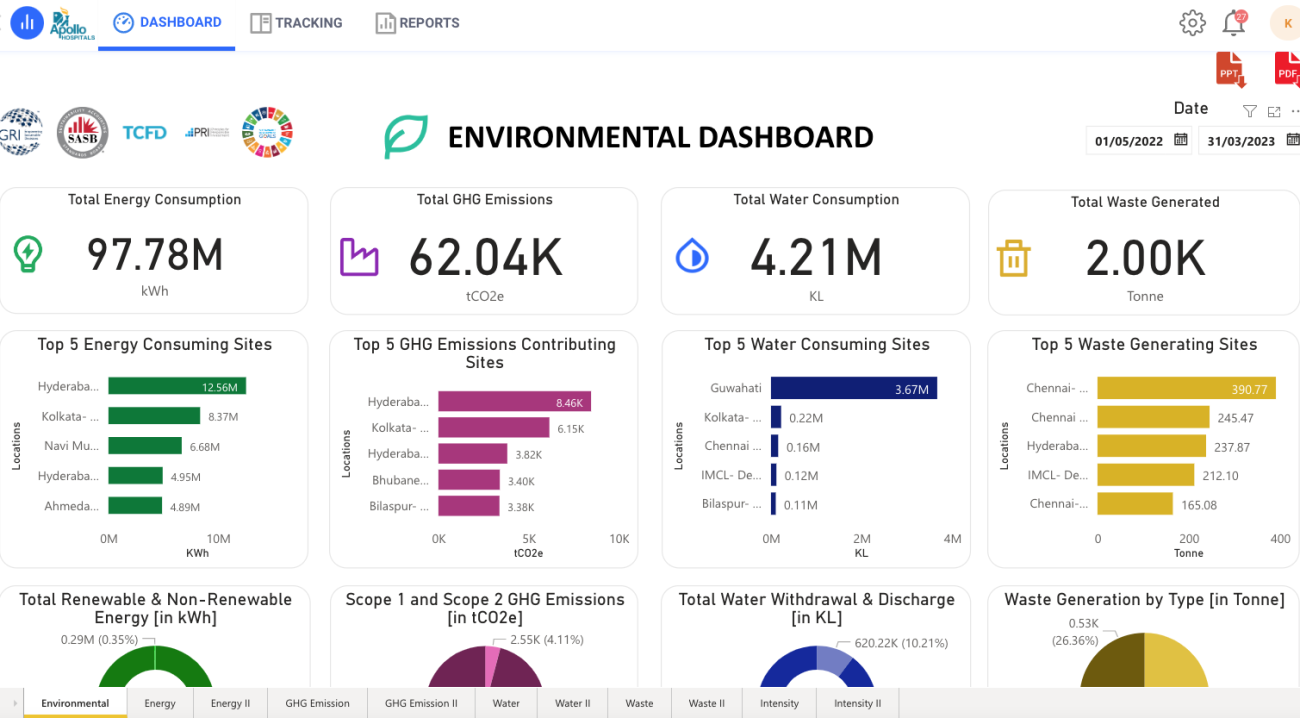
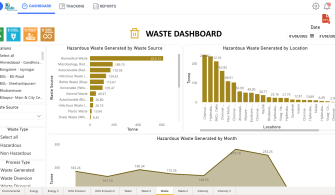
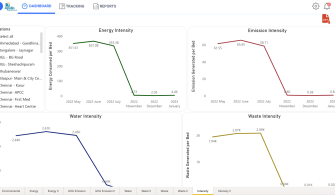
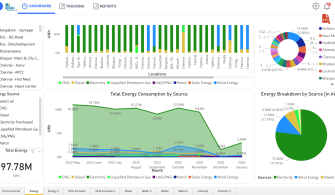
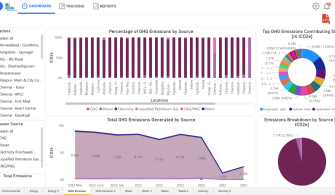
The first data sets were available in August 2022. The graphs generated from the platform helped stakeholders visualize and compare data between hospitals and better understand intensity data over a specific time period. These first visualizations helped garner enthusiasm within the team and propel this project within the team and hospitals.
Progress achieved
Developing this robust platform to measure and monitor credible and uniform data sets for emissions, waste generation, and water use across hospitals is the first significant step toward the hospital’s decarbonization journey. It has galvanized local hospital teams to set targets and activities for reductions. Further, the project has familiarized a variety of stakeholders with health care’s impact on the environment. The project is currently underway at 40 hospitals that contribute to 90% of our volumes and operations across India.
Company Secretary
"Through this project, we have created a common platform for better monitoring of our environmental footprint. This will help in creating targets as we embark on this journey of decarbonization. I am happy that this will help in our vision to have a net positive impact on our patients, the planet, and all stakeholders."
Challenges and lessons learned
A major challenge was getting a diverse group of individuals to use the platform simultaneously. When one facility had challenges adapting to the platform, we approached each individual separately to provide psychological safety when uncovering barriers. In many instances, the hospital leaders were engaged when adequate headway was not being made with data reporting. Factors that contributed to success include:
- Commitment by senior leadership and the board for the project.
- Adequate resources and infrastructure are made available.
- A governance and oversight structure and mechanism.
- Identifying local-level champions and creating buy-in from hospital leadership.
- Creating tools to increase platform uptake and improve implementation.
- Use of digital tools for troubleshooting and real-time problem-solving.
- A monitoring framework that included weekly reviews between Apollo, the service provider, and Apollo teams.
- Knowledge sharing on best practices on implementation between team members.
- Adequate feedback
- Fostering a sense of purpose for this project as part of a larger ambition to decarbonize health care.
A major lesson learned was the need for greater awareness and capacity building among the workforce to ensure smoother implementation.
Next steps
The second phase will also initiate target setting. This phase will entail reductions across parameters that are common but differentiated for each hospital (due to geographic, economic, and other variables).
During this process the hospital has received invaluable support from the Health and Environment Leadership Platform, a partner organization of Health Care Without Harm that was instrumental in fine-tuning our understanding of GHG inventorization. The forthcoming attitude of Health and Environment Leadership Platform ensured that we could tap into their global network to ensure a successful roll-out of this project.