Location: Changchun, China.
Work areas: Products, Process.
Summary: The Second Hospital of Jilin University has been actively working on sustainability for years, and has made outstanding achievements in building energy savings, medical waste management, and hazardous chemical reduction.
Initial situation
The Second Hospital of Jilin University has many years of practical experience in sustainable hospital development. By taking measures to improve management, the hospital reduced energy consumption and emissions, enhanced hospital safety, and improved the management of medical waste. The hospital also integrates the concept of sustainable procurement into overall planning and procurement processes. According to Wei Yang, vice-president of the hospital, "Building a green hospital is a new goal and challenge for the health care sector proposed by the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). A Green hospital integrates the economic, environmental and social benefits so that the hospital achieves an efficient unity.”
Proposed alternatives
1. Overall sustainable planning and design
The construction of the Yatai hospital campus was designed and planned to reserve land for future development, and maximize energy conservation and emission reductions as well as green and healthy development in the whole life cycle of the hospital. In addition, during the planning of the building, the thermal design of the enclosed structure and reasonable adjustment of heating and ventilation measures resulted in significant reductions in energy consumption.
2. Energy saving products and facilities
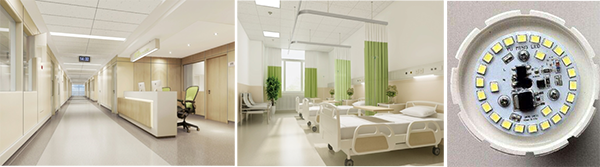
LED lighting: After evaluating the existing lighting devices, lighting range and illumination requirements, the hospital updated the lighting devices and lamps, and used devices and lamps with small volume, high energy efficiency, low toxicity and high safety as much as possible. At the same time, the most appropriate control combination was determined according to the space type, usage and opening time, including energy-saving voice control for public passage lighting, induction control for underground garage lighting, intelligent light control for function room lighting, and timing control for courtyard lighting.
After replacing the ceiling lamps, incandescent lamps, spotlights, T5/T8 lamps and other lamps with LED lamps, the hospital saved about 1,627,000 kwh of electricity every year, with an average energy saving rate of 53.5% in the lighting system (using 14 hours per day average lighting duration).
Water pipes and flow regulators: The hospital selected high-quality pipes to minimize leakage of tap water, and efficient water pumps and heat exchangers. Water saving devices are used for sanitary wares and accessories limit the outflow of sanitary wares (no toilet has a single flushing volume greater than 6L). The faucets of hand basins in clinics, public washrooms, treatment rooms and operating rooms etc. are automatically flushed by light control. The flushing valves of toilets are inductive types. In addition, the water consumption of each department is measured independently, and the water meters are set on the water pipes for measuring the water demand in each functional area, such as the air conditioning units room, cooling tower, boilers room, etc.
In 2018, compared with the same period in 2017, the volume of hospital services increased by 9.1%, but the water consumption decreased by 7.8%.
HVAC system: The frequency conversion was adopted for secondary chilled water pumps, winter chilled water pumps and cooling pumps to achieve energy savings. In the transitional seasons, the whole air system adopts the regulation mode of changing fresh air ratio, and adopts heat recovery devices to recover the exhaust energy. Hospital air conditioning equipment is all energy saving products. High-quality and efficient thermal insulation materials are used for air pipes and water pipes, and the thickness of the materials meets the energy saving requirements.
In addition, the hospital has installed an online energy consumption monitoring system to monitor the real-time energy consumption of key energy consumption departments and equipment, and established a sound energy management system for daily energy management and equipment maintenance, which can achieve 3%-10% annual energy savings.
3. Hazardous chemicals and medical waste management
The Second Hospital of Jilin University, as the hospital infection management quality control center of Jilin Province and the national medical waste management project promotion hospital, follows the management concept of standardization, reduction, recycling and non-toxic inputs. The hospital gradually replaced disposable medical supplies with qualified reusable alternatives to reduce medical waste, including disposable PPE, oral care packages and urethral catheterization kits. Biodegradable medical dressings are used to replace the traditional polypropylene non-woven dressings. Medical devices made of PVC are being phased out gradually, and the use of mercury-containing products are reduced.
Additional actions to reduce disposable medical supplies and hazardous chemicals applied by the hospital include: promote the use of reusable breathing machine screw thread pipes, stainless steel dressing bowls, oxygen humidification bottles; promote reusable slippers and reduce the use of shoe covers; install EOW disinfection system to reduce harmful chemical residues; reduce the use of the disinfectant glutaraldehyde.
In addition, the hospital purchased a solvent recovery machine for pathological waste liquid, which can separate and purify the generated xylene and ethanol waste liquid, remove tissue debris, paraffin and other impurities in the waste liquid, and realize resource recovery and reuse. This can not only reduce the use of organic solvents such as xylene, but also save a lot of money needed for the treatment of xylene (hazardous waste).
Information about the organization
The Second Hospital of Jilin University, under the management of the National Health Commission, is a Grade III Class A general clinical medical college integrating medical treatment, teaching, scientific research and rehabilitation. The hospital has a total building area of 439,000 square meters, and 315,000 square meters under construction. It has 2789 open beds and 3 hospital campuses.