Location: Beijing, China.
Work areas: Policy.
Summary: Production of a Sustainable Procurement Evaluation Guidance for health care institutions. The Guidance evaluates three elements of a health care institution’s procurement practice: management measures, key products and services, and supplier management.
Initial situation
China has been developing green public procurement policies since approximately 2004, largely through the labeling of energy efficient and environmentally friendly products. Public hospitals are encouraged to abide by government green procurement policies, but the above-mentioned labeled products merely cover hospital logistics and administrative areas, and are not specialized to cover hospital-specific needs such as machinery or other medical supplies. In order to create a systematic tool to guide and evaluate Chinese healthcare institutions’ sustainable procurement, Rock Environment and Energy Institute (REEI) collaborated with the China Environmental United Certification Center (CEC) to develop a Sustainable Procurement Evaluation Guidance for Healthcare Institutions in 2019, which is a sub-project supported by SHiPP.
Proposed alternatives
The guidance followed the key principles outlined in the Sustainable Procurement Guidance ISO 20400:2017, such as accountability, transparency, full and fair opportunities, and respect for the interest of stakeholders.
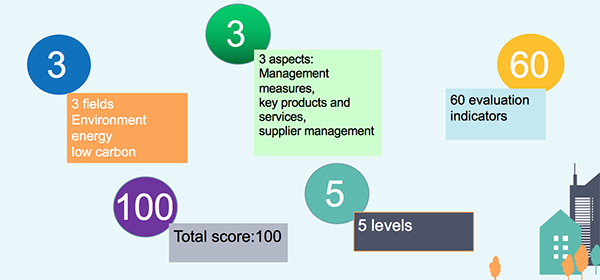
The guidance targets healthcare institutions such as hospitals and health centers, but excludes healthcare administrative agencies. The Guidance evaluates three elements of a healthcare institution’s procurement practice: management measures, key products and services, and supplier management. It is composed of a guidance text and an evaluation form. In total, the guidance has 60 evaluation indicators, and a total score of 100 divided into five levels.
Progress and benefits
By the end of 2020, the following progress has been achieved:
- The Guidance including Guidance text and an evaluation form was launched.
- The Guidance has been shared with groups working on sustainable healthcare during domestic meetings.
It is expected that the Sustainable Procurement Evaluation Guidance for Healthcare Institutions could fill the above-mentioned policy gap by creating a tool to guide and evaluate Chinese healthcare institutions’ sustainable procurement covering different categories of products and services.
Implementation process
To develop the guidance, major activities included literature reviews, and hospital interviews, drafting the guidance, holding expert consultation meetings, testing the guidance in hospitals, revising, and finalizing the guidance.
The development of the Guidance required both expertise on procurement and standard setting, and knowledge of specific products. For example, when setting indicators for sterilization or anesthetics, we needed to understand the availability of alternatives and the feasibility of alternatives.In addition to interviewing hospitals, it was also necessary to consult with experts in the specific product fields.
Next steps
After the launch, the team made up of REEI staff and CEC professionals have been working on promoting the Guidance during various events and projects. For example, we introduced the Guidance in the activities of the PVC Infusion Sets Substitution Pilot Project and in a webinar on the Health Care Decarbonization Roadmap in 2021.
Information about the organization
CEC is a technical supporting institution of China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment, specializing in standard development and certification. Since 2005, CEC has worked on green government/public procurement, and has been providing policy research and technical support on the topic for the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Ecology and Environment. CEC has also participated in UNEP SPP co-lead work since 2019.